Fyrox Game Engine 0.30
I'm happy to announce that Fyrox 0.30 has been released! Fyrox is a modern game engine written in Rust, it helps you to create 2D and 3D games with low effort using native editor; it is like Godot, but in Rust. This is the biggest release of the engine since the very beginning. This release is mostly focused on animation, editor, audio, quality-of-life improvements.
# Animation
Animation system was significantly improved, and now it should be much easier to create complex animations that are used all over the place in the modern game development.
# Root Motion
Root motion is a special animation technique of motion transfer from a root bone to a physical capsule that moves characters in games. It is used to prevent "floating" or "sliding" effect; to perfectly match capsule motion with the motion from the animation. To get better understanding of how it works, check the video:
As you can see, root motion significantly improves overall animation quality: feet matches the ground and the motion looks natural.
# Blend Space
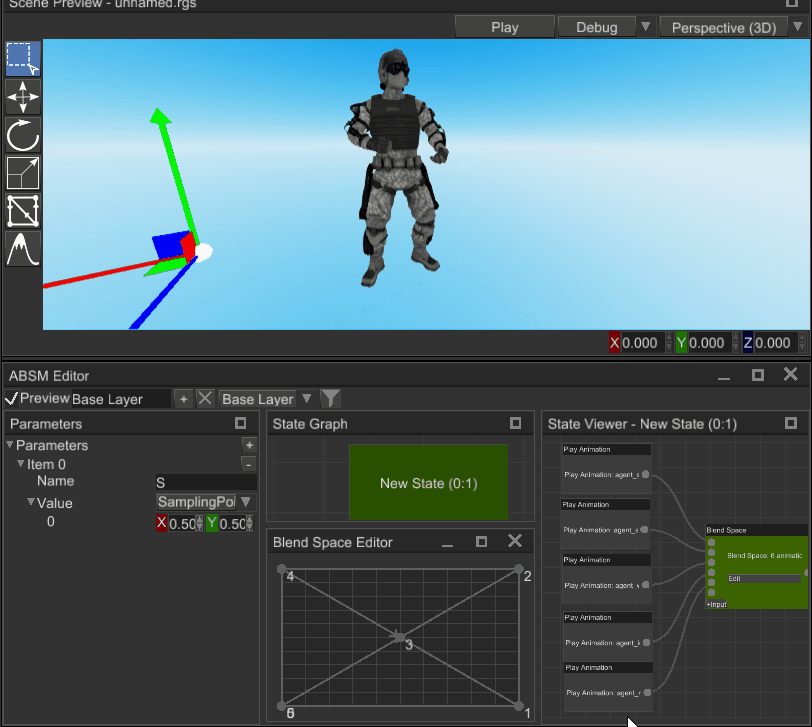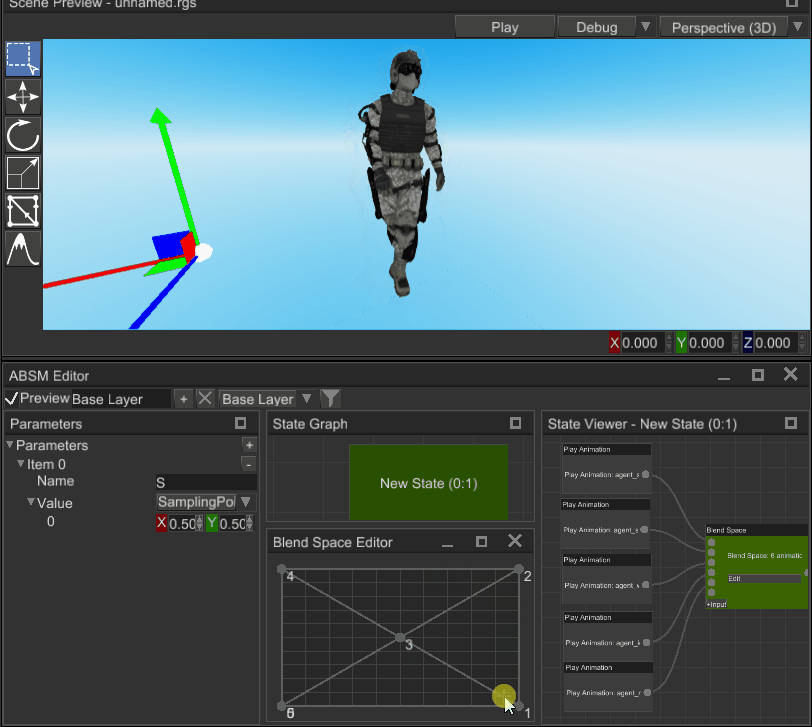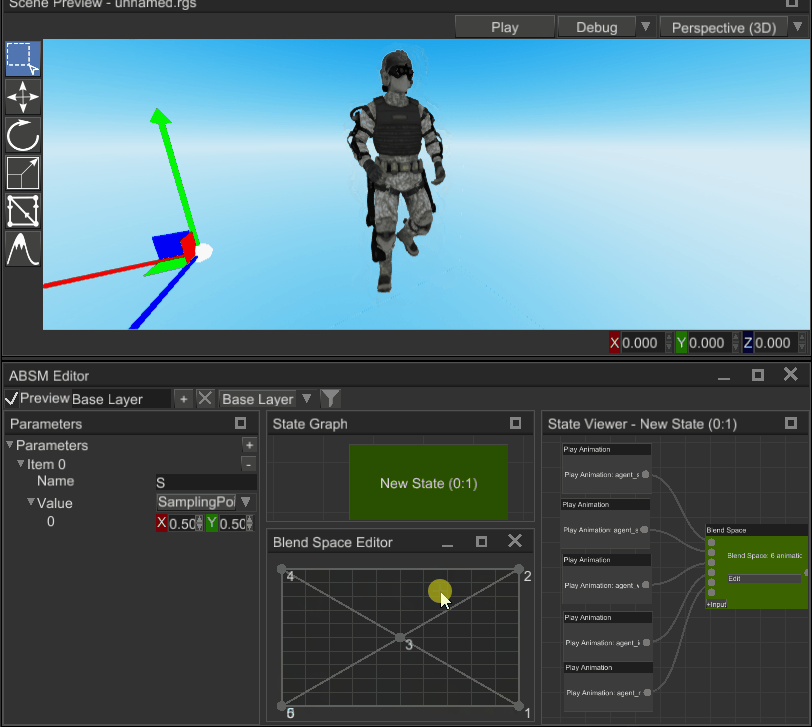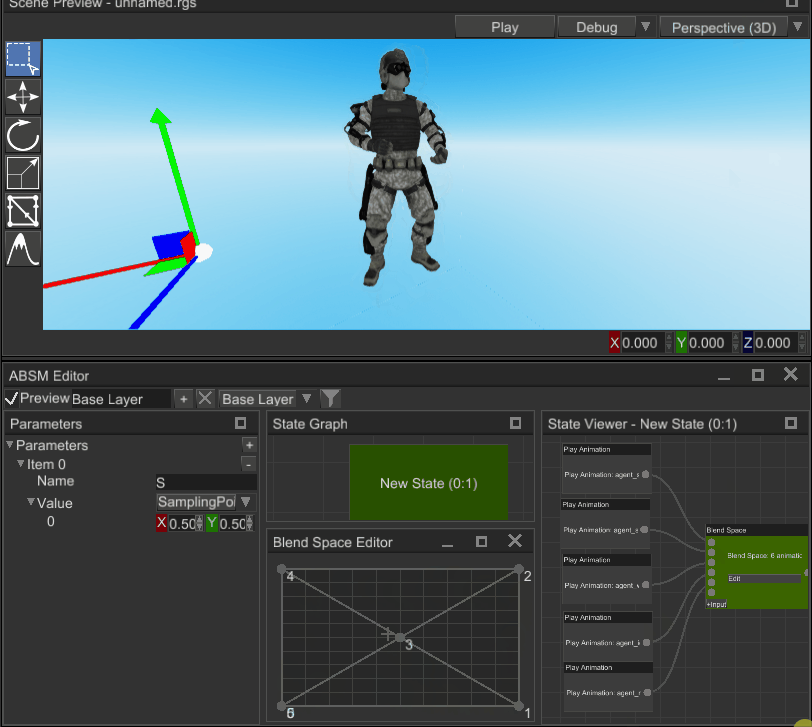
Blend space is an animation blending technique which allows you to blend multiple animations into one based on two numeric input parameters (sampling point). Blend space consists of any number of points, located in the value space; these points are triangulated:
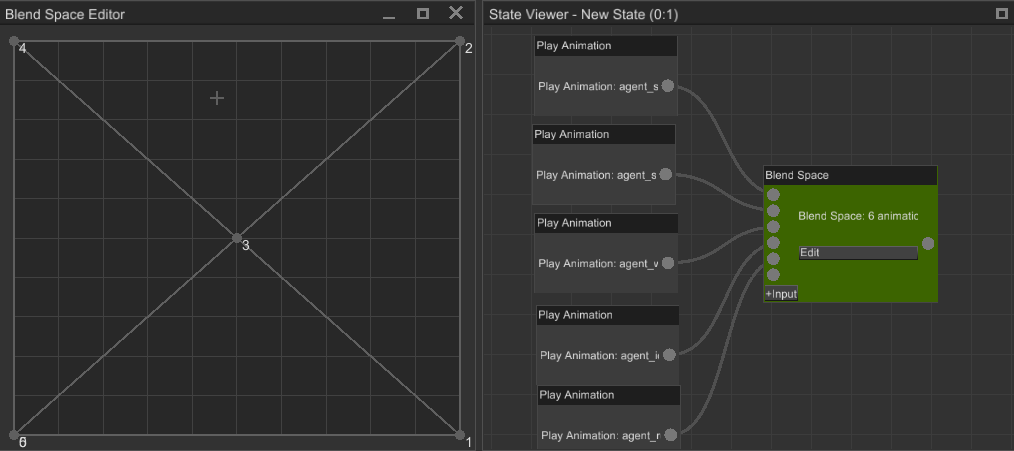
To blend animation, you need to pass sampling point in (visualized as a crosshair on the screenshot) and the blend space will calculate weights for three animation poses around the sampling point. See the gif above to get better understanding.
Where this technique is used? In pretty much any relatively complex modern game. It is used mainly to blend locomotion animations based on two parameters: speed and direction. For example, on the X axis you can have direction angle and on Y axis - speed. Then you put desired animations on the blend space, and it will blend everything accordingly to speed and direction: if a character moves fast, then running animation will prevail, if it needs to run left - direction will be -1 and running left animation will prevail and so on. It is a very powerful and flexible technique, that helps achieving naturally looking animations on most conditions.
# Blend Shapes
Blend shapes allows you to dynamically change 3D meshes; they are widely used in games to create facial animation, to dynamically add details to character body parts, etc. It is quite simple, yet very powerful mechanism, that opens a wide range of possible uses: you can create cut-scenes directly on the engine where your characters will speak using pre-defined set of shapes associated with visemes (opens new window). You can also use this to create characters creator for your game - all you need to do is to specify a set of offsets for desired parts of face and then allow a player to mix these parts with any proportions they like. In other words, actual use of this functionality is limited by your imagination.
# Ability to Animate Material Properties
It is now possible to animate properties of any material, it adds a lot of control for various visual effects that use custom shaders. Animation editor is now able to bind to material properties, making something like this possible:
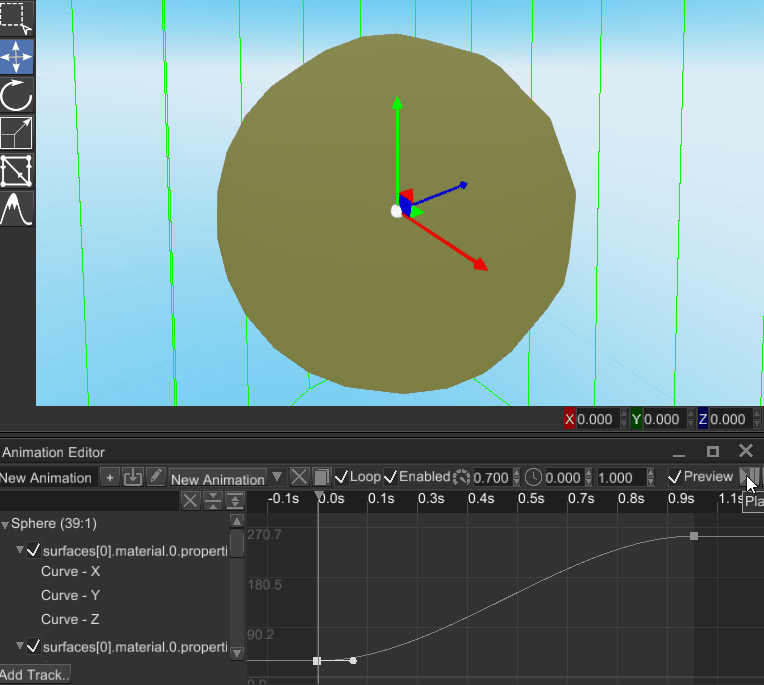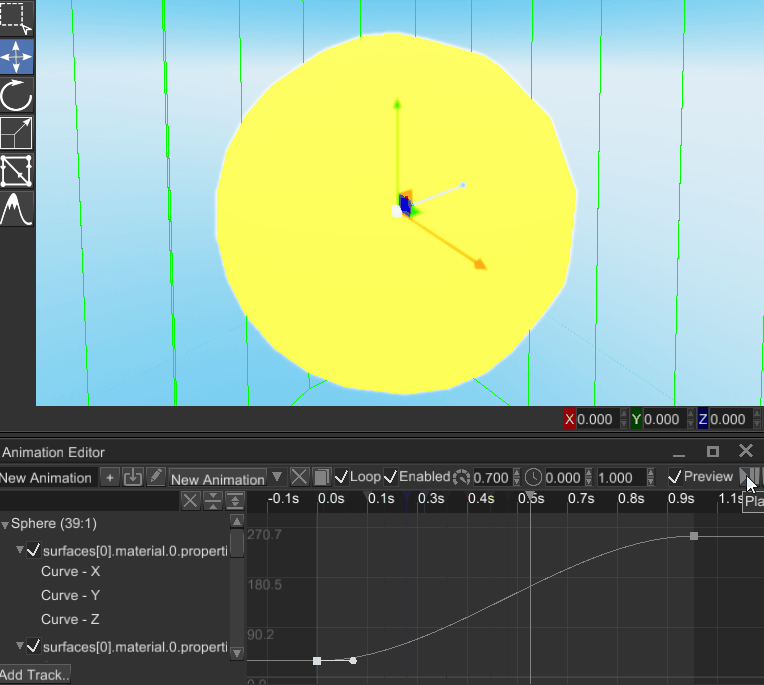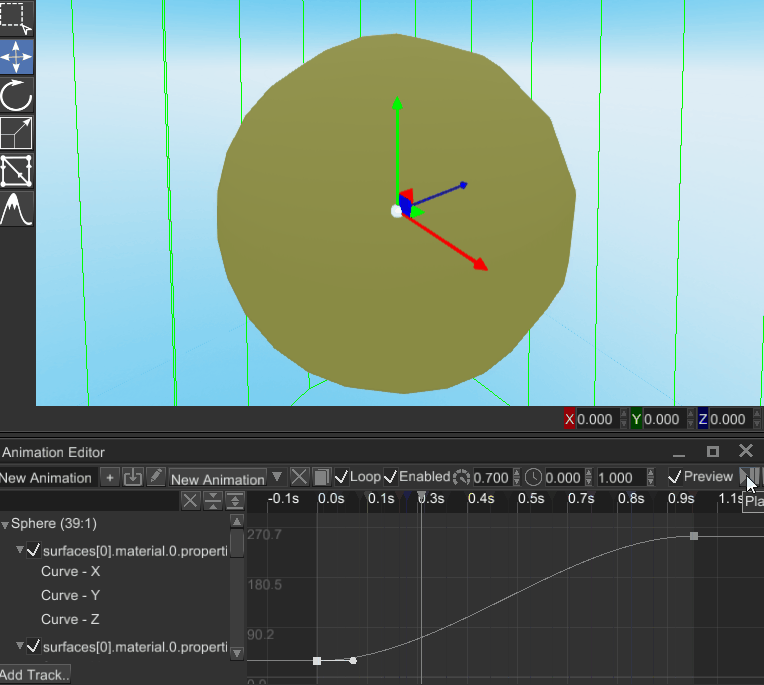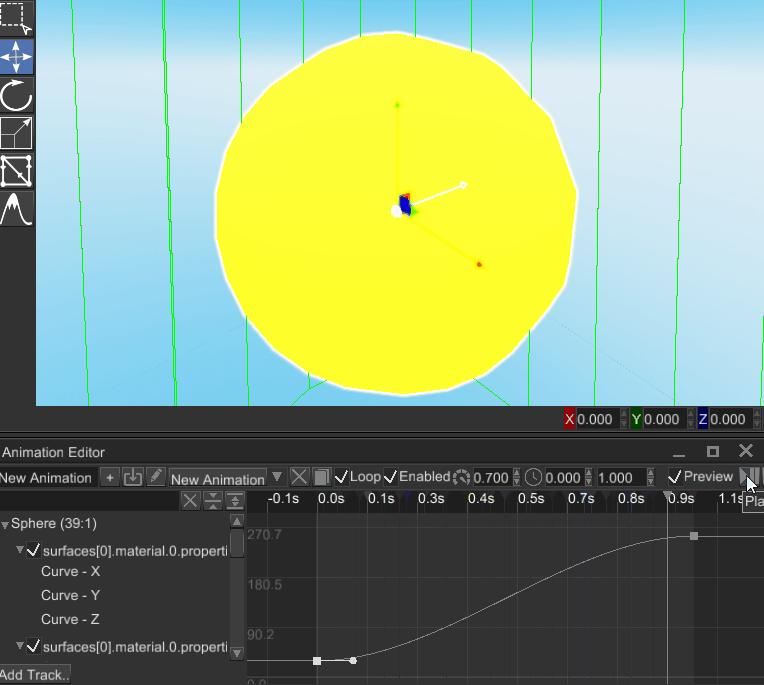
This can be applied to pretty much any numeric shader uniform, which adds an ability to create any kinds of visual effects.
# Compound Rules For ABSM Transitions
In previous versions of the engine, transitions in animation blending state machines were driven directly
by a single bool property. In simple cases it was enough, however combining multiple variables was
problematic, because you need to introduce another variable for the result and use it in your ABSM. This
sometimes resulted in exponential growth of the amount of variables. In this release, the issue was solved
by introducing computational graph for logical expressions:
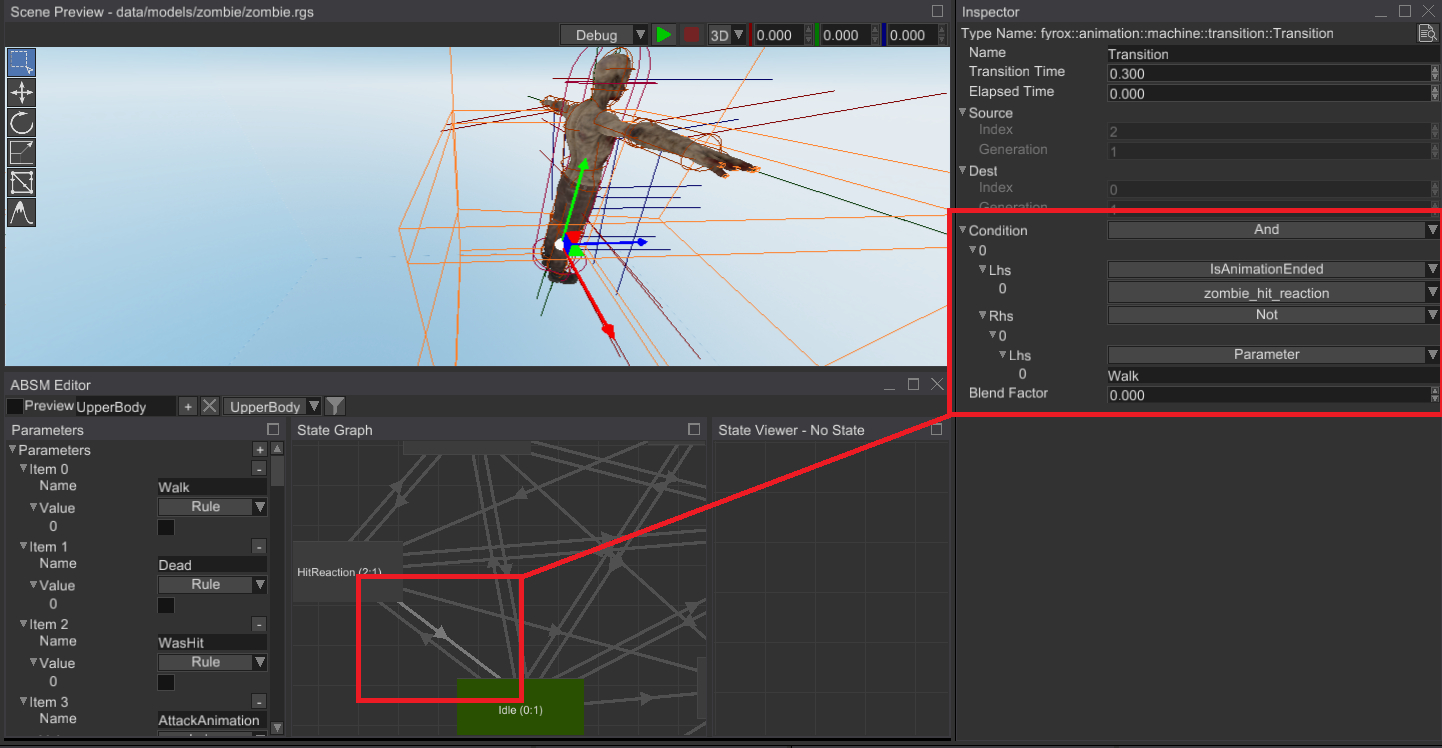
Now you can combine multiple logical values using standard logical operations such as AND, OR, NOT, XOR.
Previous functionality of fetching single bool parameter, was moved to Parameter.
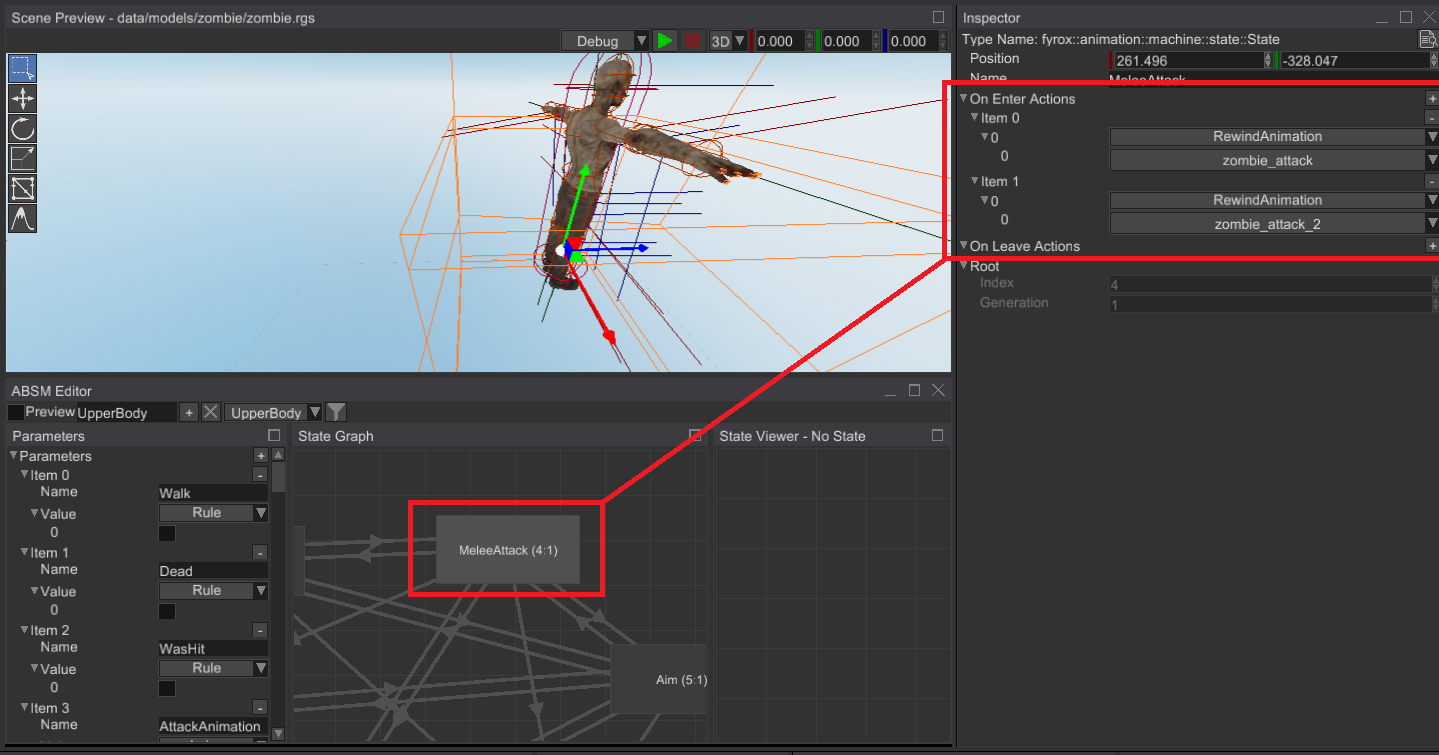
# Animation-Related Actions for Enter/Leave State Events
It is now possible to rewind, enable, disable specific animations when entering/leaving ABSM state. It is very useful if you have a one-shot animation (for example, for a melee attack) and you want it to play again when some state was activated.
# Other Animation System Changes
Animation blending state machine event ActiveStateChanged is now allows you to fetch previously active
state when a transition to another state was done.
Previously, ABSM editor had a bug where activation of a state/transition on one layer was shown on the layer being edited, causing confusion while debugging ABSMs.
Animation blending performance was slightly improved by removing unnecessary calculation steps.
# Reflection Refactoring
Main downside of the previous version of reflection system in the engine is that it does not support reflection of types
with interior mutability. You simply cannot "inspect" fields of a of type with interior mutability
(such as Mutex<T>, RwLock<T>, RefCell<T>, Arc<Mutex<T>>, etc.), because anything that is located
inside these types require to hold some kind of lock while accessing the internals (MutexGuard<T> in case of
Mutex, Ref<T>/RefMut<T> in case of RefCell and so on).
Interior mutability support in reflection system is crucial for animation system of the engine. Its main usage is to animate numeric parameters of renderer materials. This ability allows you change shader uniforms via standard animation pipeline.
The API of Reflect trait was changed
completely (opens new window).
Now, instead of returning references immediately, every function that previously returned references now has
additional parameter. This parameter is a reference to a closure that allows you to do something with a reference
to inner value. Such approach allows to hold mutex lock (and analogues) while doing something with the inner data.
Another important reflection system improvement is hash map support. This functionality was added to have an ability to animate properties of materials via engine's animation system. This was a pretty easy change, but it added more flexibility to the reflection system.
# Android Support
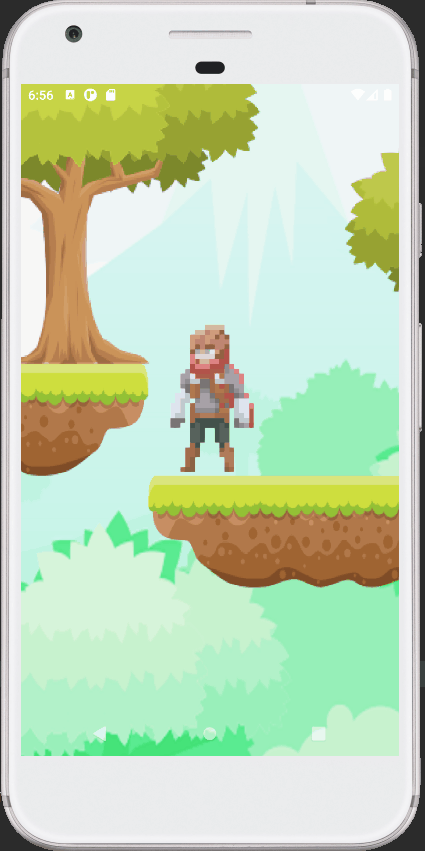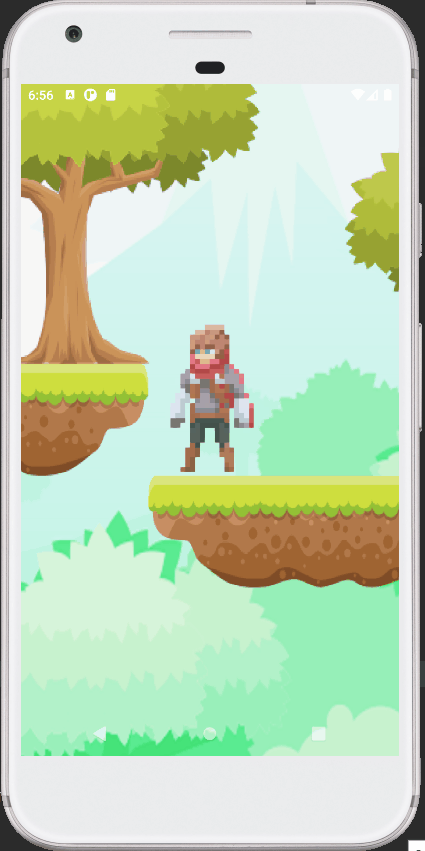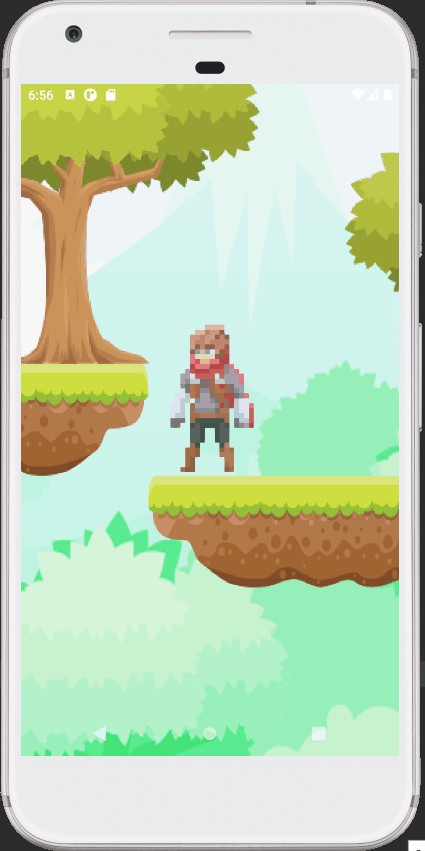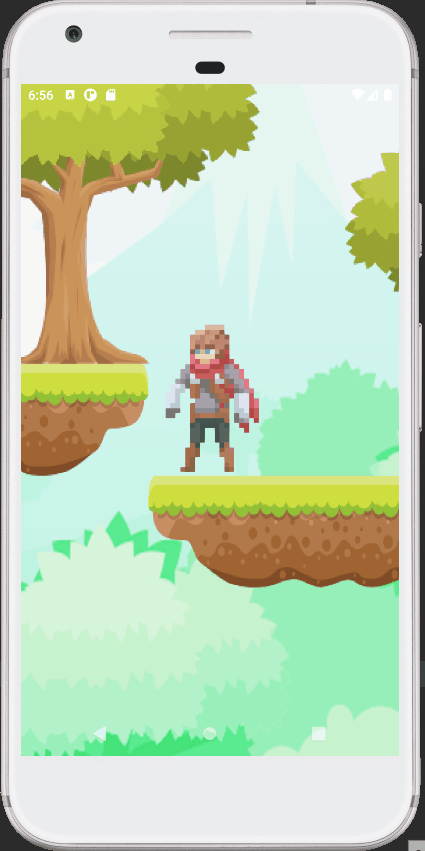
Android support was requested multiple times (opens new window) already and after ~1.5 years from the first request it is finally added. Current renderer implementation, however, is not great for mobile devices, because it uses graphics rendering techniques that are PC-oriented, so rendering performance is quite bad if you use complex 3D graphics. However it is more or less fine on 2D graphics. There's a separate task (opens new window) about writing a separate, lightweight renderer for mobile devices. Keep in mind, that you need to have a relatively new device (2015+), that supports OpenGL ES 3.0 to get the engine working on mobile devices.
# "Headless" Mode
Game servers usually do not render anything, nor playing any sounds. Even main application window can not exist. Previously, it was somewhat impossible to fully prevent the engine from creating the window, render graphics and output sounds. Now it is possible, to initialize the engine in "headless" mode without the window, renderer and audio system initialized. It can be put back into standard mode at any time.
# Audio System Refactoring
Previously, the sound system supported direct output of sound samples to an audio playback device with some effects that can take samples from sound sources and put processed samples in the audio playback device. It worked ok for most cases, but it was quite rigid and effect management was a pain. To add more flexibility in audio processing pipeline there was added two new entities: audio buses and audio bus graph.
# Audio Bus
Audio bus is a sound processing unit that takes samples from various sound sources, applies zero or more effects to the samples and sends the samples either to an audio playback device or some other audio bus (see the next section). Effect list includes: lowpass filter, highpass filter, bandpass filter, allpass filter, low and high shelf filters, reverberation.
# Audio Bus Graph
Audio bus graph is a set of audio buses connected with each other: one audio bus could be a source of samples for another audio bus or for an audio device:
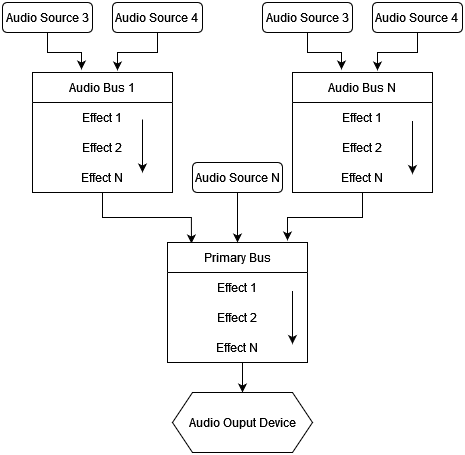
Such structure provides high flexibility, allowing you to create complex processing steps for the sound in your game.
In action the graph looks (sounds) like this:
# Other Audio Improvements
Sound panning in HRTF mode was fixed (left was right and vice versa). Fyrox now uses TinyAudio (opens new window)
crate as a sound output backend. This is a new, tiny crate that serves a single purpose - make audio output as simple
as possible. Also, compared to cpal, this crate it does not have weird sound artifacts on WebAssembly and builds fine
on Android platform.
# Scene Graph Improvements
Scene graph has some improvements as well.
# Ability to Change Graph Root
Sometimes there's a need to change scene graph root (for instance, to reorder the children nodes in a different
manner) and it was impossible to do in the previous version of the engine. This is now possible to do in the
current release. This could be done either from code by using Graph::change_root/change_root_inplace or
in the editor by right-clicking a node in the World Viewer and pressing Make Root.
# Navigation Mesh Node
Navigational meshes are now scene nodes and part of the scene graph. Previously, navmeshes were stored in a separate storage which caused a lot of issues with property inheritance, scene integrity checks and many other small issues.
Navigation Mesh panel in the editor was made floating by default and it automatically appears when you select the node.
# Improved Graph Search
It is now possible to do up-search in the Graph. It could be useful to find a parent entity of with a
particular component and get some data from it. Every graph search method is now returns a tuple
Option<Handle<Node>, &Node> - as you can see they now also returns a reference to found nodes. This is
useful to prevent re-borrowing after you found a node.
# Message Passing for Scripts
Message passing is a mechanism that allows you send some data (message) to a node, hierarchy of nodes or the entire graph. Each script can subscribe for a specific message type. It is efficient way for decoupling scripts from each other. For instance, you may want to detect and respond to some event in your game. In this case when the event has happened, you send a message of a type and every "subscriber" will react to it. This way subscribers will not know anything about sender(s); they'll only use message data to do some actions.
# Determinism for Particle Systems
Previously, particle systems used global pseudo-random numbers generator (PRNG), which resulted in non-deterministic behavior. Now, each instance of particle system has its own PRNG and saves its seed, which makes behaviour of particle systems deterministic. It is even possible to rewind particle systems to a particle time and the result will always be the same (until PRNG implementation is not changed).
# Physics
Previously, any user force or torque applied a to rigid body (via respective methods) will remain the same until you change it again, this behavior is now changed - the engine resets it to zero.
Terrain height map colliders now takes node scaling into account.
# Rendering
Renderer was refactored to gather graphical data from scene nodes. Previously, the renderer gathered the data
by itself, but it was very restrictive and now it calls Node::collect_render_data for every node to generate
render batches. Also, frustum culling is now done on scene node side - the renderer only provides enough info
for clipping and you're free to implement it in any way you like. The refactoring is not fully done yet, some
parts of the renderer still manually collects render data from scene nodes of specific, hardcoded types. This
refactoring improves flexibility of the rendering.
# Bone Matrices
Previous versions of the engine had a limit of 64 bones per mesh surface, now it is pretty much unlimited ( standard shaders, however, still has 255 bones limit because it stores bones indices in a single byte). Previous limit was forced by the limited amount of shader uniforms, the new limit, is only limited by a data type used to store the numbers and the amount of VRAM.
# Offscreen UI Rendering
Offscreen UI rendering (rendering into texture) is now compatible with HDR pipeline, previously the textures looked pale.
# Lightmapper Fixes
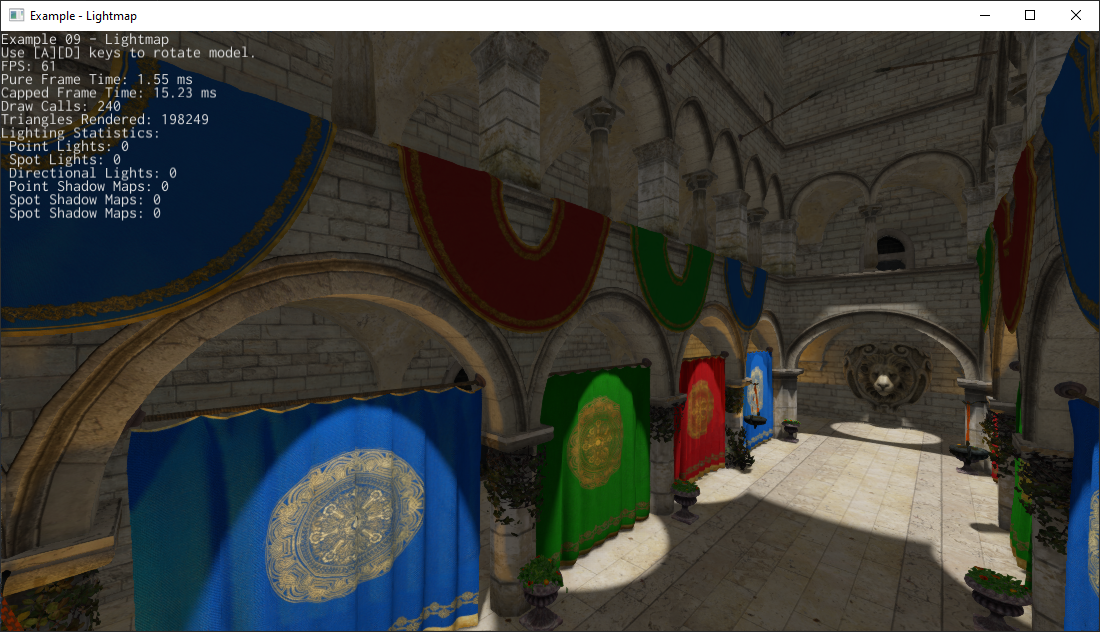
As you might know, Fyrox has built-in lightmapper and it is integrated in the editor. For quite a long time, there was a bug that corrupted GPU vertex buffers when preparing second UV map for light maps. Which resulted in weird graphical artifacts. Also, when saving a scene with light map, node handles weren't correctly remapped thus leading to panic when trying to load such scene. Now these bugs are fixed you can use lightmapper normally.
# HDR Fixes on OpenGL ES
For about a year, graphics looked pale on WebAssembly compared to PC. That's because of differences between sRGB frame buffers behavior on OpenGL and OpenGL ES. sRGB frame buffers on OpenGL does not change input values from shader and write values as is (unless you turn sRGB conversion manually) and convert them to linear when reading from sRGB textures. On OpenGL ES, however, such conversion is on by default in both ways and it led to pale-colored output image on platforms such as WebAssembly.
# UI Improvements
UI's DrawingContext is now able to draw arcs and rounded rectangles.
# Generic Vector<T,N> editor
fyrox-ui now have generic version of SVector<T, N> editor. Also, this new editor supports limits (min, max),
and step that can be supplied to it using reflection (min, max, step attributes respectively). This can
be useful in your scripts: now your vector parameters can use these attributes.
# NumericUpDown Widget
Values of NumericUpDown widget can now be changed by mouse dragging:
# Editor Improvements
FyroxEd is a native scene editor of the engine, it has lots of various improvements and new features as well.
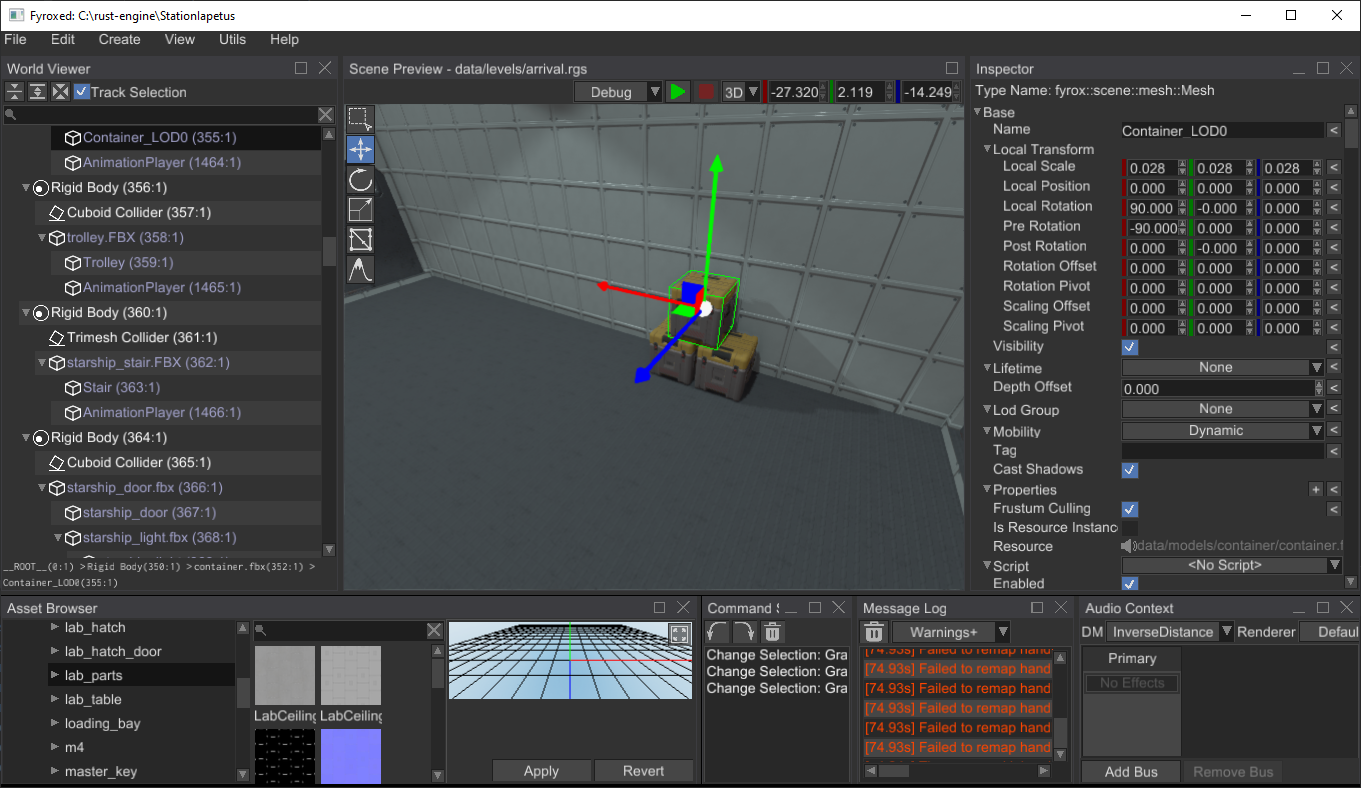
# Editor Restyling
The editor now has more cleaner and modern user interface:
The old version for comparison:
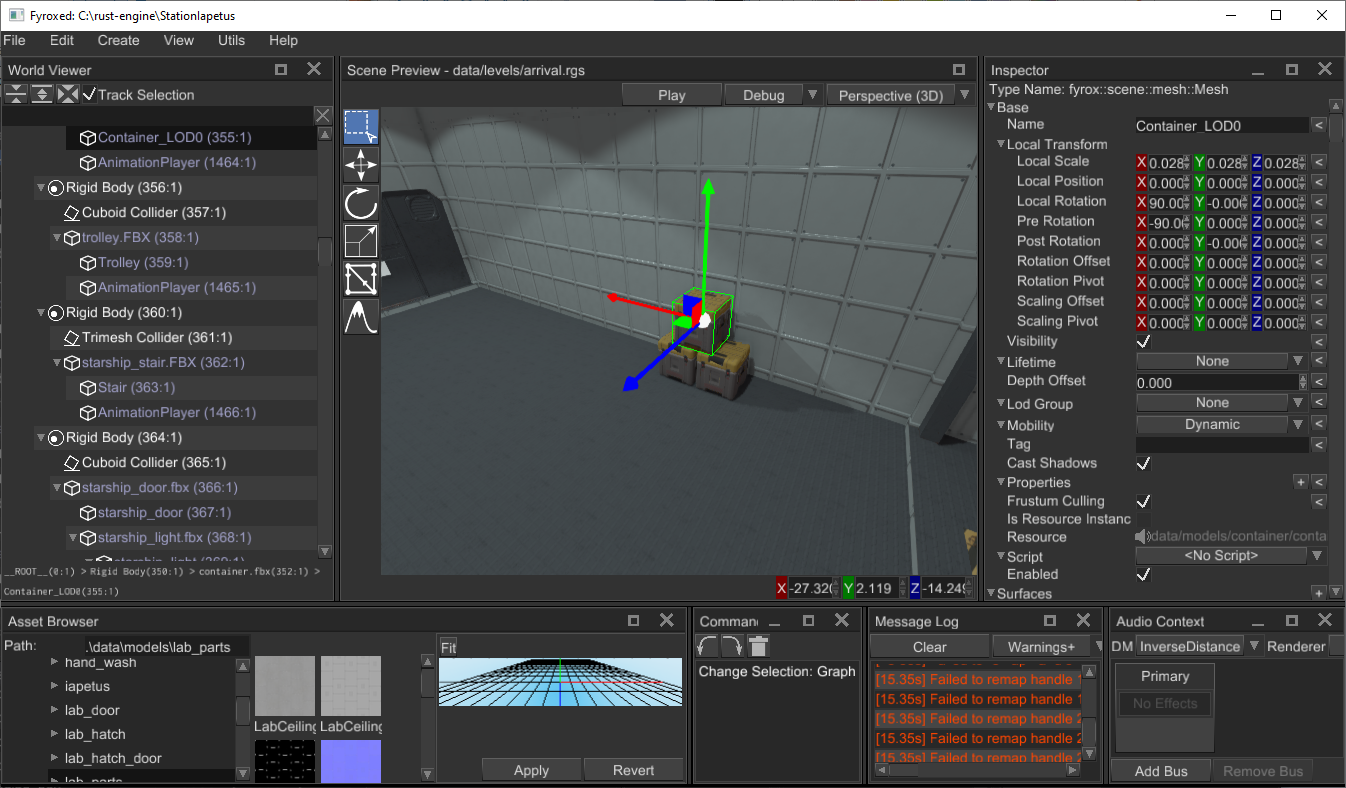
The new style does not have radical differences with the previous one - it just improves existing style, to make it a bit more attractive.
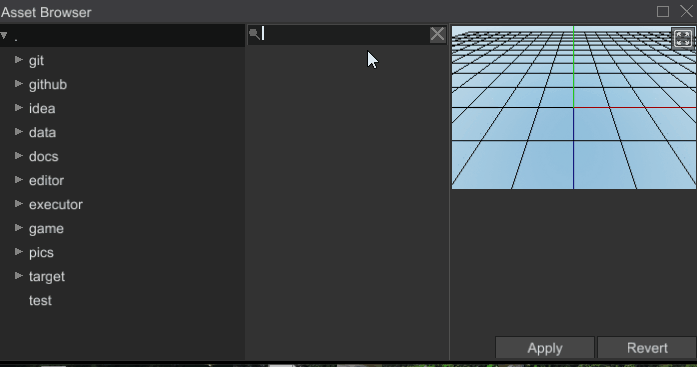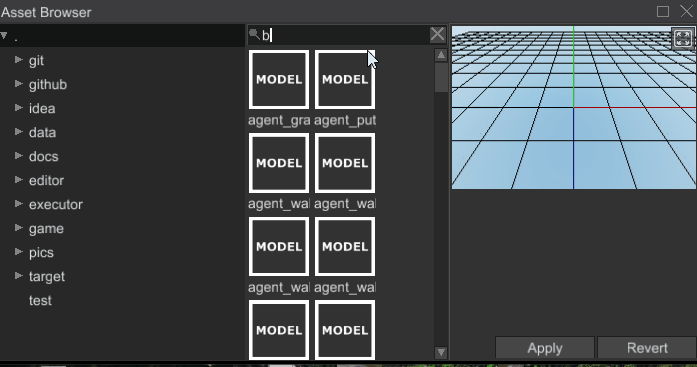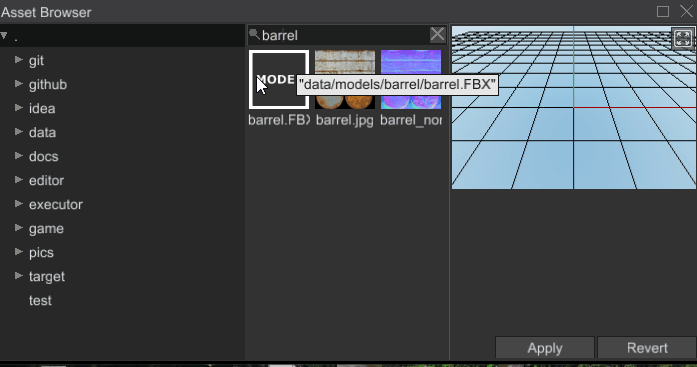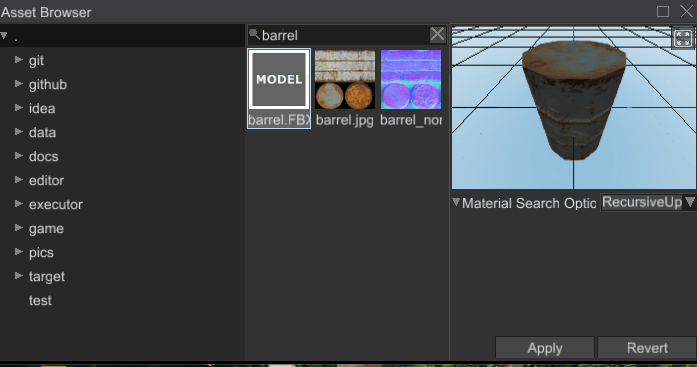
# Ability to Search Assets
Asset browser is now able to search assets by name:
# Audio Improvements in the Editor
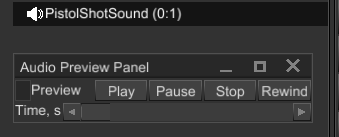
Sound management in the editor now much more predictable and convenient. Previously, any sound in Playing state would immediately start playing after you load a scene in the editor, making pretty much impossible to create sound effects. It is now fixed, every sound is now not updating until you start previewing it. This can be done in a new audio preview panel:
 .
.
To activate it, all you need to do is to select a Sound node. Then you need to click on Preview checkbox
and the sound will start playing. Any changes made in this panel will not be recorded in the scene, you
can play with the sound as you want to.
# Color Gradient Editor
For a long time there was no property editor for Color Over Lifetime field of particle systems. The type of this
field is ColorGradient which allows you to define a set of color points and fetch intermediate values at any
position at the gradient. Now, the editor has property editor for ColorGradient and it works like so:
# Animation Editor
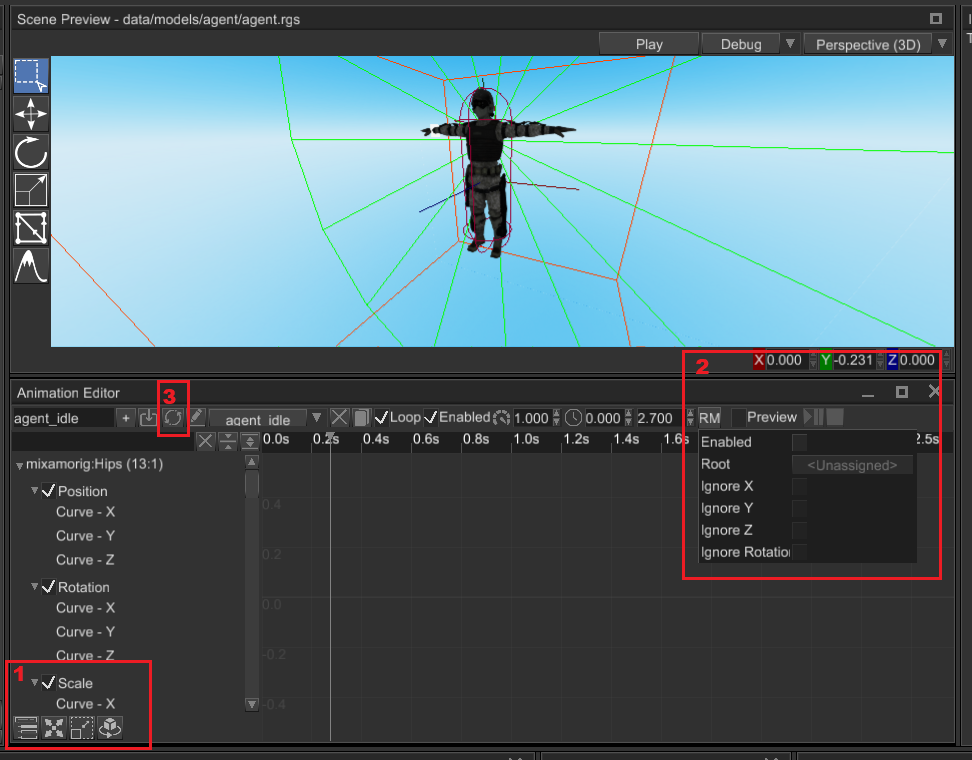
The animation editor has many major quality-of-life improvements:
- Ability to create special bindings to position/scaling/rotation properties of a scene nodes. Such bindings are much faster in terms of performance and widely used in pretty much any animation.
- Ability to enable root motion and set its settings, like position and rotation filtering.
- Ability to reimport animation - this is useful when you need to replace an animation, but preserve its handle. It is very useful if you already have an Animation Blending State Machine that uses an animation that you want to change.
Imported animations are now enabled by default, previously they were imported as disabled which could lead to confusions.
Animation editor now validates all tracks of your animation, showing every track that has any issues, which may include deleted scene node, changed property type, missing property binding. It it very useful for rapid development - any issues are instantly highlighted helping you to fix it as fast as possible.
# Help Menu
It is now possible to open the book (opens new window) and the API reference (opens new window) from the editor via Help menu:
# Asset Browser
Asset Browser now shows texture resources as a textured quad, which is much more convenient than small texture preview in the asset list.
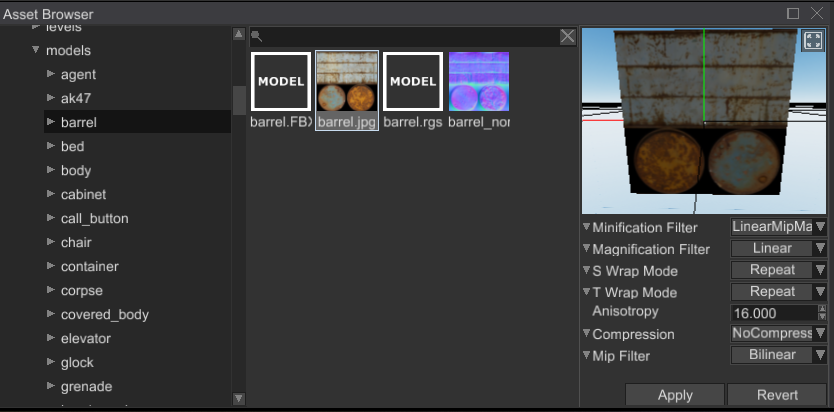
Sound resources will now automatically play (once per selection) when selected in the asset browser. This way you can "preview" the sounds before using them.
# Editor Performance Improvements
There was a nasty performance degradation bug, that caused the editor to work more slowly over time, especially
when switching between multiple entities too frequently. The cause of bug was context menu system of the UI
framework. Context menus are "standalone" entities, they're not attached directly to a widget, instead widgets
just use their handles. Also, the same context menu can be shared across unlimited amount of other widgets.
Usually, when you deleting UI node, fyrox-ui deletes all children nodes, but since context menu is not a child
node, they weren't deleted, thus leading to tons of context menus left "alive". Now this bug is fixed, by using
a special "shared handle", which is essentially just a Rc<Handle<UiNode>>. It has a custom destructor that
sends a WidgetMessage::Remove message to the context menu when there's no more strong references to it.
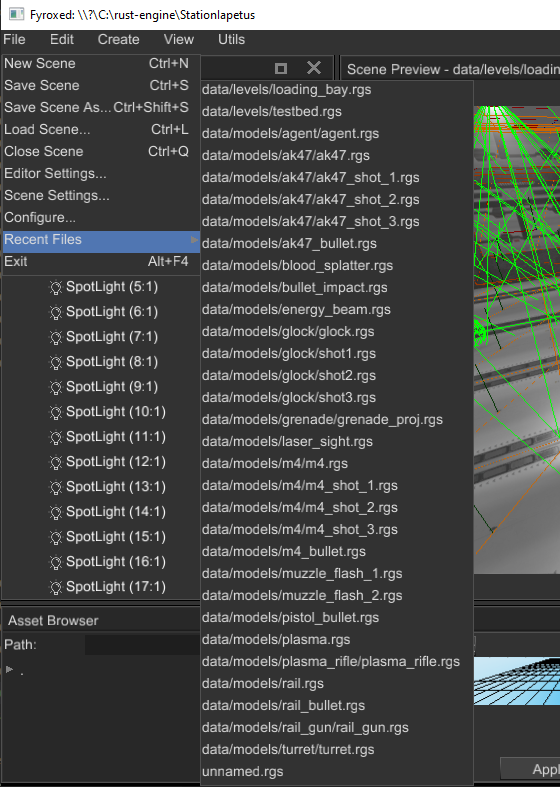
# Recent Files
Recent files list in the editor now sorted and non-existing files are auto-removed from it:
# Other Editor Changes
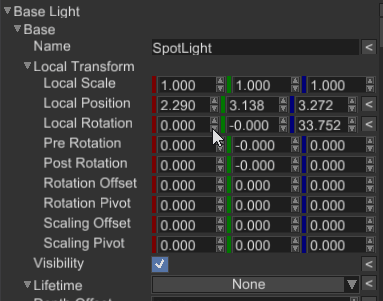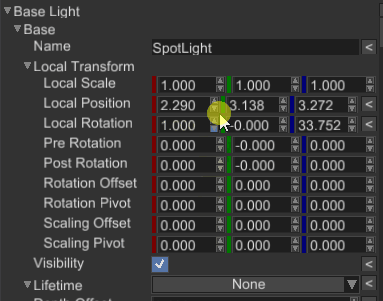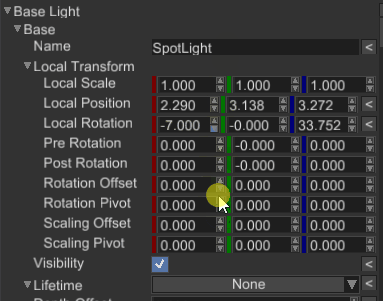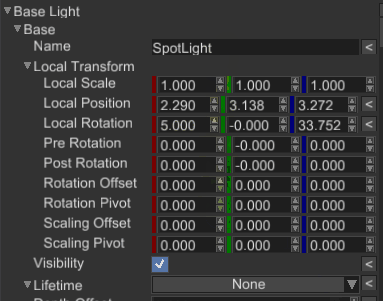
In the editor it is now possible to change the size of light pictograms - their default size could be too big in specific cases.
Lifetime field is now visible again in the Inspector, previously it caused crashes and was temporarily
hidden. It is now possible to create temp nodes in the editor, that will be automatically deleted when the
lifetime reach zero.
It is now possible to rewind particle systems during preview mode - it removes all generated particles and starts generation over.
Fixed a bug in the sound preview panel, it was possible to infinitely play a sound, even when preview mode is disabled.
It is now possible to show/hide debug shapes (for lights, cameras, etc.) in the editor.
Editor's window position and size is now saved in settings file and restored on next load. It saves extra clicks when opening/closing the editor in rapid development.
# Resource Management
Resource management was significantly improved in this release. It includes user-defined resource, resource dependency graph and various bug fixes.
# User-Defined Resources
For a long time, Fyrox was able to manage only four hard-coded resource types (textures, models, shaders, curves) and it was quite restrictive. Now you can create custom resource types. It could be useful to access specific data using engine's resource manager. Custom resources has a few major advantages over manual resource management via direct files access:
- Since Fyrox resource system is asynchronous, your resource can be loaded in separate worker thread which speeds up loading (since it may run on a separate CPU core).
- You can access your resources from the Asset Browser and assign their handles to scripts directly from the editor.
- File access for resource management has an abstraction, that unifies the access over all supported platforms. This
means that you don't need to use
fetchAPI directly, if you're targeting WebAssembly platform, or useAssetManageron Android.
For more info see the respective chapter (opens new window) in the book.
# Resource Dependency Graph
Resource dependency graph allows you to collect all resources used by a resource. It could be useful when you
need to find unused resources, copy all dependent resources, etc. You can use this functionality in the editor
by right-clicking on a resource and then clicking Dependencies:
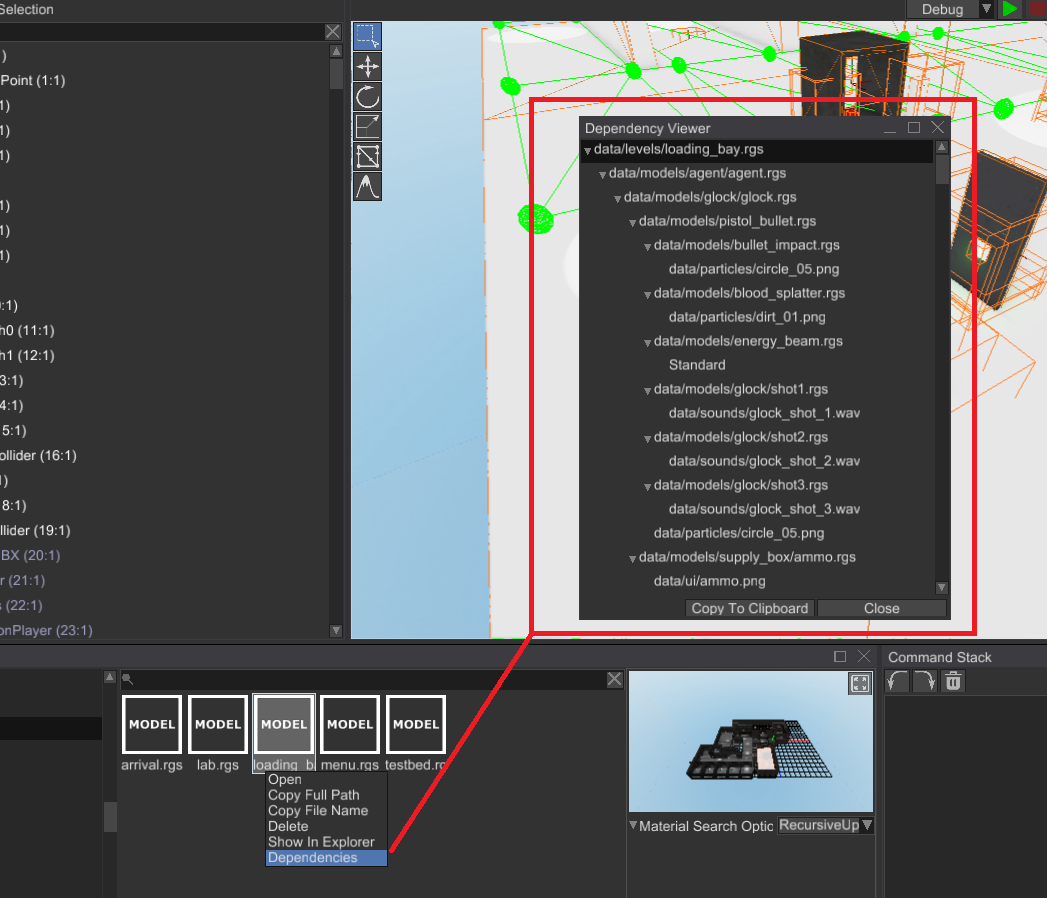
# Automatic Resource Handle Restoration
When the engine saves a scene that has resource handles, those handles saves only path to resources, not the actual content. When loading the same scene, the engine re-loads all resources, but all handles scattered around must be restored manually to point to actual resource data. This is now fixed, the engine will use reflection to iterate over each field of every scene node and restore the handles.
# Other Resource Management Changes
It is now possible to fetch standard shader names. Sound nodes now have validation, which check if a sound source has missing sound buffer.
# Property Inheritance
Property inheritance is used to propagate changes of unmodified properties from a prefab to its instances. For example, you can change scale of a node in a prefab and its instances will have the same scale too, unless the scale is set explicitly in an instance. Such feature allows you to tweak instances, add some unique details to them, but take general properties from parent prefabs.
In this release its reliability was significantly improved. This allowed to not serialize content of non-modified properties (since their data is stored in parent prefab) which resulted in significant decrease of disk space usage for derived prefabs.
# Terrain
Terrain node was changed significantly in this release. These changes will be a strong basis for further improvements.
# Ability to Change Height Map and Mask Size
It is now possible to change height map and mask sizes. It could be useful if you created large terrain and want to make it smaller and vice versa. Height maps or mask will be resampled to the new size, which could result in data loss if you decreasing the size.
# Improved Chunking
Previously, it was impossible to add or remove terrain's chunks which was very limiting and it was basically impossible to add a new editable portion to existing terrain. For example, if you made a terrain and decided extend it from any side to add more content there - it was impossible, now, however, this issue is solved and terrain could be extended from any side.
# Level-of-detail
Terrains now has powerful level-of-detail system implemented. It is now possible to create giant terrains (64x64km) and render them in about a millisecond.
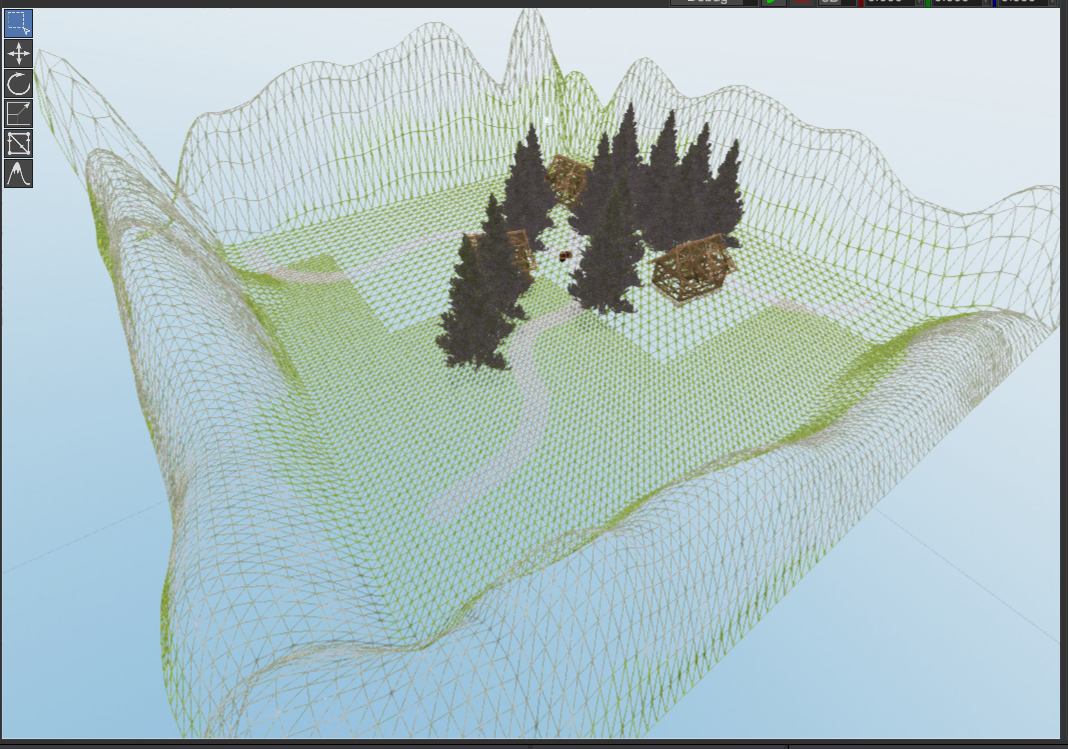
# Ability to Flatten Slopes
It is now possible to flatten terrain slopes by using special brush mode. It is very useful to create plateaus, which can then be used to place some game objects on it.
# Ability to Use Texture as Height Map
This is very simple way to create terrains - all you need is a grayscale image that can be made in any graphics
editor and you need to assign it to heightmap field of a chunk:

# Other Terrain Improvements
Fixed terrain editing in the editor; its material property is now exposed in the Inspector. Terrains geometry is now update immediately when doing changes to the height map.
# Side Projects
Station Iapetus (opens new window) is sci-fi shooter that is built using the engine. Over the past month it is again in active development, @mrDIMAS is preparing basic game mechanics (mostly on a testbed level). Once they're done, he will start making new game levels. Old game levels can still be loaded, but their interactive entities (such as doors) will not work as expected.
# Full List of Changes in Random Order
- Ability to change graph root to arbitrary graph node.
- Ability to change graph root in the editor.
- Optional checkerboard background for
Imagewidget. - Simplified animation blending.
- Mutable access to curve key's value.
- Added property validation for the animation editor.
- Track validation for the animation editor.
- Ability to set widget's tooltip via message.
- Correctly sync track names in the animation editor.
- Ability to change target nodes on animation tracks.
- Preserve parent when extracting a sub-graph from a graph.
- Refactored editor scene structure to allow modifying the root node.
- Play sound buffer resource when inspecting it in the asset browser.
- Show textured quad in resources previewer when inspecting a texture.
- Configurable scroll speed for
ScrollViewerwidget + speed up scrolling 2x. - Helper methods to quickly check a resource state.
- Helper methods to access script components faster.
- Improved range property editor.
Enter Statefor state menu in absm editor. Works the same as double click, removes confusion for ppl that does not get used to double-click on things.- Leave preview mode when closing or changing scenes in the editor.
- Prevent panic when trying to generate random number from an empty range.
- Serialize delay line samples as POD array.
- Optional ability to save current scene in text form for debugging.
- Do not render disabled sprite nodes.
- Fixed property inheritance subtle bugs.
- Do not allow revering a property value in the editor if there's no parent.
- Do not save content of non-modified inheritable variables.
- Fixed directional light docs.
- Fixed
Node::is_x,as_x,as_x_mutmethods. Graph::try_get_script_of + try_get_script_of_mutmethodsBase::root_resource- allows you to find root resource in dependency graph.- Prevent deadlock on self-referencing model resources
- UUID for widgets.
- Save editor's window position and size into editor's settings.
- Apply local scaling of terrain to heightfield collider.
MachineLayer::is_all_animations_of_state_ended- Ability to fetch all animations of a state in ABSM layer.
- Added
IsAnimationEndedcondition for ABSM transitions. - ABSM state actions. Allows you to rewind/enable/disable specific animations when entering/leaving a state.
- Fixed incorrect "state enter" event sent from source instead of dest.
- Added a collection of built-in resources for resource manager. This collection is used on resource deserialization step to restore references to built-in resources.
- Pre-compile built-in shaders on engine startup.
- Ability to change camera zoom speed in the editor.
Plugin::before_rendering- Matrix storage cache to prevent driver synchronization steps.
- Persistent identifiers for render entities.
- Improved deserialization performance.
- Use
fast_image_resizecrate to generate mip maps (which gave 5x performance boost). - Configurable filter for mip-map generation for textures.
- Fixed tooltip position - it now does not go outside of screen bounds.
- "Immutable collection" reflection attribute for collection fields that prevent changing collection size.
- Ability to get typed data of specific mip level of a texture.
- Ability to fetch specific mip level data of textures.
- Ability to set height map of terrain chunks directly from an image.
- Dependency graph visualizer for asset browser.
- Resource dependency graph.
- Ability to flatten terrain slopes.
- Return local height value at intersection point in ray-terrain test.
- Cleaned editor's command API.
- Removed visibility cache.
- Ability to index graph with
Handle<T: NodeTrait> Handle::transmute- Doc comments support for reflection.
- Show doc comments for selected entity in a separate window.
- Moved logger to
fyrox_core. - Resource system refactoring to support user-defined resources.
- Blackboard for visitor to pass arbitrary data when serializing/deserializing.
- Added missing recalculation of terrain bounding box.
Texture::deep_cloneLog::verify_messageR32F+R16Ftexture formats.data_of_typemethods to reinterpret inner texture data storage to a particular type.- Debug drawing for scene nodes.
- Configurable polygon rasterization mode for scenes (gbuffer only).
- Ability to set polygon rasterization mode to select between solid and wireframe rendering.
- Force
Framebuffer::draw_xmethods to accept element range to draw. - Proper culling for terrains.
- Refactored rendering: scene nodes can now supply renderer with data.
NodeTrait::collect_render_datais now used to supply renderer with data. - Batch generation is now done on per-camera (which includes light sources for shadows) basis.
- Added a method to link nodes while keeping child's global position and rotation.
- LODs for terrains.
- Limits for collider shape values.
- Added doc example for
Graph::begin_multi_borrow. - Fixed samplers type collision when rendering with materials with different sampler types.
- Unbind texture from other samplers when setting it to a new one.
- Fixed half-float textures + fixed volume textures mip maps.
RGB16Ftexture format.- Use texture-based matrix storage for "unlimited" bone matrices. Raises matrix count per surface from 64 to 255 for standard material.
- Fixed texture alignment issues.
- Use correct sampler index when changing texture data.
- Set new mip count for texture when changing its data.
- Fixed texture binding bug.
- Warning instead of panic when there's not enough space for bone matrices.
- Rename
visitor::Nodetovisitor::VisitorNodeto prevent confusing import in IDEs. InheritableVariable::take- Ability to change size of terrain height map and layer masks.
- Ability to add chunks from any side of the terrain.
- Fixed crash when deleting a navmesh edge.
- Improved package description.
- Make navmesh panel floating by default + open it when a navmesh is selected.
- Navigational mesh refactoring.
- Navigational mesh scene node.
- Pass light intensity into lightmapper.
- "Headless" mode for
Executor- suitable for server-side of multiplayer games. - Added editor's window icon.
- Blend shape support.
- Changed sidebar to be inspector in the view dropdown menu.
- Tweaked step values for transform properties.
- Limits for vec editor.
- Generic
Vector<T,N>property editor. - Added support for min, max, step property attributes for vecN.
- Ability to create/destroy audio output device on demand.
- Migrate to
tinyaudioas audio output backend - Use
RcUiNodeHandlefor context menus. This ensures that context menu will be destroyed when it is not used anymore. - Fixed multiple lightmapping issues.
- Fixed incorrect
sRGBconversion for WASM. - Android support.
- Ability to run the engine without graphics/window/sound by making these parts optional.
- Update to latest
winit+glutin. - Ability to change value in
NumericUpDownwidget by dragging - Removed "Scene Graph" item from world viewer + made breadcrumbs much more compact.
- Put interaction mode panel on top of scene previewer.
- Added ability to search assets in the asset browser.
SearchBarwidget.- Ability to hide path text box in file browser widget.
- Hide path field in the asset browser.
- Tooltip for asset items in the asset browser that shows full asset path.
- Improved simple tooltip style.
- Optional ability to suppress closing menus by clicking on non-empty menu.
- Added
No Scenereminder in the editor and how to create/load a scene. - Editor UI style improvements.
DrawingContext::push_arc+push_rounded_rect- Ability to enable/disable debug geometry for camera/light sources.
- Show indices of input sockets of ABSM nodes.
- Keep animations enabled on import.
- Blend space support.
- Added help menu (with
Open BookandOpen API Referenceitems) - Ability to create special (much faster) bindings to position/scale/rotation of nodes in the animation editor.
- Ability to reimport animations in the animation editor.
- New example: render to texture.
- Audio bus graph.
- Root motion support.
- Audio panel rework to support audio bus graphs.
- Sound effect API improvements.
- Keep recent files list sorted and up-to-date.
- Fixed incorrect sound panning in HRTF mode.
- Ability to get unique material instances when cloning a surface.
- Validation for sound node
- Audio preview panel
- Do not play sounds in the editor automatically. Sounds can only be played from the audio preview panel instead. fixes the issue when you have a scene with multiple sounds, but since they're playing, their playback position changes and these changes sneak in the saved scene preventing from defining strict playback position
- Ability to partially update global properties of a hierachy of nodes.
- Do not crash if a root node in the previewer died.
- Fixed deadlock when selecting object's property in animation editor.
- Ability to set pre-generated particles in particle systems.
- Provided access to standard shader names.
- Print texture resource name when failed to create its GPU version.
- Rebuild terrain's geometry on deserialization.
- Automatic, reflection-based resource handle mapping.
- Ability to ignore some type when doing property inheritance.
- Support for hash maps in the property selector.
- Expose material fields via reflection.
- Keep flags of
ScrollBarMessagewhen responding to value message. - Delegating implementation of
Debugtrait forImmutableString. - Added reflection for hash maps.
- Reflection system refactoring to support types with interior mutability (
Mutex,RefCell, etc.) - Ability to rewind particle systems to a particular time.
- Determinism for particle systems.
- Fixed preview mode for particle systems.
- Ability to "rewind" particle systems in particle system control panel.
- Fixed
ParticleSystem::clear_particlesfor emitters that does not resurrect their particles. - Fixed potential panic in formatted text on missing glyphs.
- Supply
PluginContextwith performance statistics for the previous frame. - Property editor for
ColorGradients. - Simplified
color_over_lifetimefield in particle systems. - Improved color gradient API.
- Fixed incorrect activation of transition/states during the preview mode in the ABSM editor.
- Compound conditions for ABSM transitions
- Fixed off-screen UI rendering compatibility with HDR pipeline.
- Refactored scene node lifetime management - this mainly fixes the bug when a node with
Some(lifetime)would crash the editor. The same is applied to play-once sounds.Node::updatenow does not manage node's lifetime anymore, instead there'sNode::is_alive. - Fixed incorrect handling of user-defined forces of rigid bodies. A body was pushed continuously using previously set force.
- Configurable size for light pictograms in the editor
ActiveStateChangedevent now contains both previous and new states.- Message passing for scripts with multiple routing strategies
Graph::find_map/find_up_map/find_up_by_name- Improved
Graph::find_xmethods - returnsOption<(Handle<Node>, &Node)>now, that removes another borrow if there's a need to borrow it at a call site.
# Support
If you want to support the development of the project, click one of the links below. Preferable way is to use Boosty (opens new window) - this way the money will be available for the development immediately. Alternatively you can can use Patreon (opens new window), but in this case the money will be on-hold for unknown period of time (details are here (opens new window)).
Also, you can help by fixing one of the "good first issues" (opens new window), adding a desired feature to the engine, or making a contribution to the book (opens new window)